Conservation of Linear Momentum
Conservation of Linear Momentum: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Explosion of a Projectile in Its Path, Conservation of Linear Momentum, Variable Mass System & Theory of Rocket Propulsion etc.
Important Questions on Conservation of Linear Momentum
A 600 kg rocket is set for a vertical firing. If the exhaust speed is 1000 the mass of the gas ejected per second to supply the thrust needed to overcome the weight of rocket is :
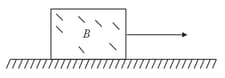
A block B is pushed momentarily along a horizontal surface with an initial velocity v. If is the coefficient of sliding friction between B and the surface, block B will come to rest after a time
If the force on a rocket moving with a velocity of is , then the rate of combustion of the fuel is:
A shell is fired from a canon, it explodes in mid air, its total :
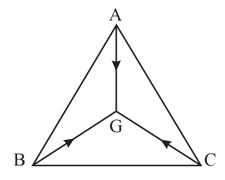
Three particles and of equal mass move with equal speed along the medians of an equilateral triangle as shown in figure. They collide at the centroid of the triangle. After the collision, comes to rest, retraces its path with the speed . What is the velocity of ?
A shell of mass is at rest initially. It explodes into three fragments having mass in the ratio . If the fragments having equal mass fly off along mutually perpendicular directions with speed , the speed of the third (lighter) fragment is:
A particle, moving horizontally, collides perpendicularly at one end equal mass and placed on a smooth horizontal surface.
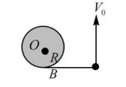
A smooth horizontal plane supports a fixed vertical cylinder of radius and a particle is attached to the a horizontal thread as shown in the figure. horizontal velocity is imparted to the particle, then during the subsequent motion (assume particle can move freely in horizontal plane)
A rocket is set for a vertical firing. The exhaust speed is . To give an initial upward acceleration of , the amount of gas ejected (in ) to supply the needed thrust will be (Take )
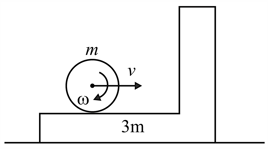
A '' shaped wedge of mass having sufficiently long horizontal base is placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the diagram. A thin ring of mass and radius is set in motion on the rough horizontal part of the wedge with a linear velocity and angular velocity , such that . Ring collides with the smooth vertical part of wedge and collision is perfectly elastic. After a sufficiently long time, the final speed of the wedge is . Find the value of . [Assume wedge does not topple due to collision]
The figure shows a block having a small basket in it and an small inclined plane is rigidly attached to the block. The combined mass (including incline plane) of all these is . Initially they are at rest. Now identical balls each of mass are thrown horizontally with velocity (with respect to ground) which strike the inclined plane and then are collected in the small basket. Assume that in the basket balls come to rest with respect to basket.
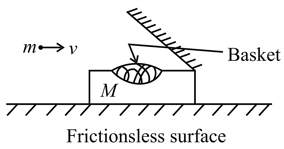
Two balls and of masses and respectively are lying on a smooth surface as shown in the figure. Ball A hits the ball (which is at rest) with a velocity Such that B just reaches the highest point of inclined plane.
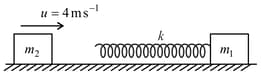
A block of mass is connected with ideal spring of spring constant and kept at horizontal frictionless surface as shown in the figure. The block is moving with velocity towards block and are the final speed of the block and respectively.
The end of a chain of length and mass per unit length , which is piled up on a horizontal platform is lifted vertically with a constant velocity by a variable force Find as a function of height of the end above platform.
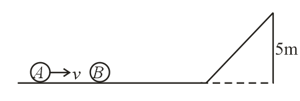
As shown in the fig. all surface are frictionless and block is released from top of the incline then

Spring is compressed between two blocks of masses and placed on a horizontal frictionless surface. When the blocks are released. The blocks travel distance and respectively before coming to rest. The ratio is
A nucleus disintegrates into two nuclear parts which have their velocities in the ratio . The ratio of their nuclear sizes will be
The difference between the working of a jet and a rocket is
A man throws a ball straight up. The ball has a momentum in the vertically upward direction.The principle of conservation of momentum demands that the earth has
A jet engine works on the principle of
